System Design 101 : From a Beginners POV
I really like to talk about system with people who are either really great at designing it or with peeps who are just getting started with this topic. For me System is very much vast topic to learn and be mastery off, as in tech there will always be something new to explore and learn.
System Design is not about writing the code, its about figuring out how everything fits together. Its the process defining the architecture, components, modules, interfaces and data flow of a system to meet specefic requirements
 Small Components of Chat Application
Small Components of Chat Application
Introduction
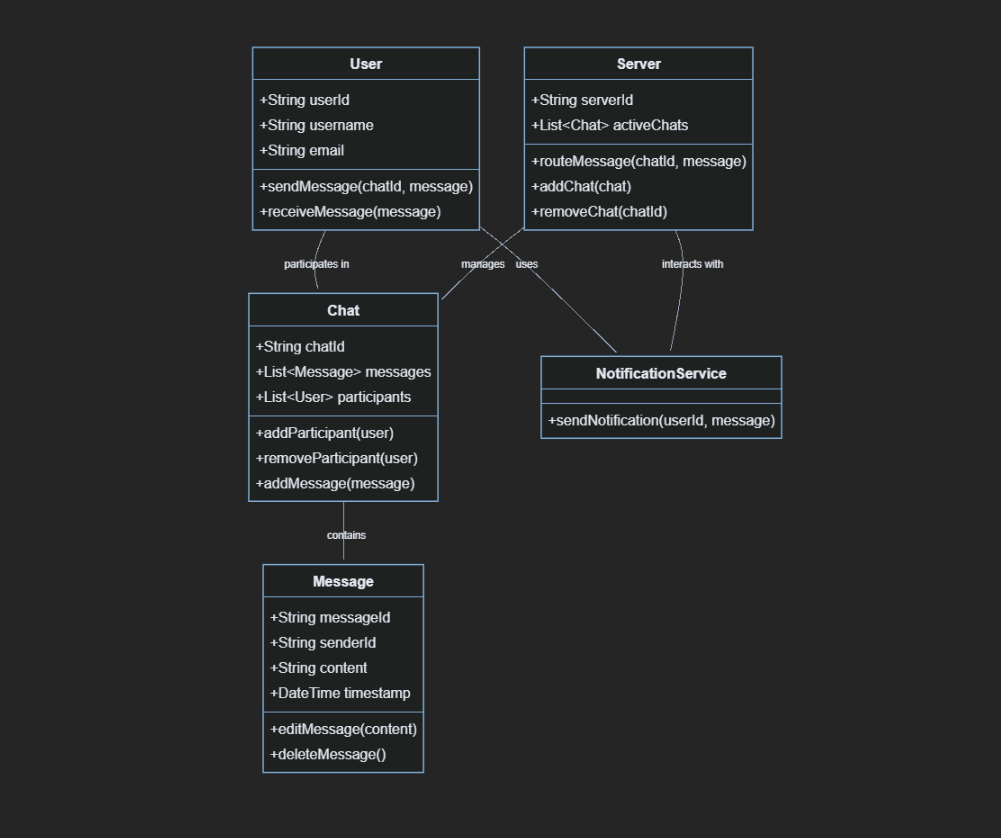
I am building a platform which is LeetSys, a small app running on a single server. When a user [client] wants to see questions, thier browser sends a request to our server. The server process this request, which then fetches posts from a database. The database sends back a response with the question data.
This client-server model is the foundation of web interactions. Requests and responses are typically sent over HTTP(HyperText Transfer Protocol), a stateless protocol that governs how clients and server should communicate. But soon LeetSys started to gain attraction among the users and gained a lot of virality, more and more users joined. So we need to scale our small app to millions of requests which can't be handled by our single CS[Client => Server] model
Scaling our platform
Our server is overwhelmed, and load times are sky rocketting. So what to do now ? We can do two things either opt for
Vertical Scaling : Which means we have to upgrade our server with more CPU, RAM and storage, this will boost performance temporarily, but there's a ceiling to how powerful a single server can get, and will cost us wayyyy to much !!
Or we can opt for
Horizontal Scaling : Instead of one bigg server, we deploy multiple smaller servers, each handling a subset of requests. This is more cost-effecient and effective, but introduces way more complexity to our systems.
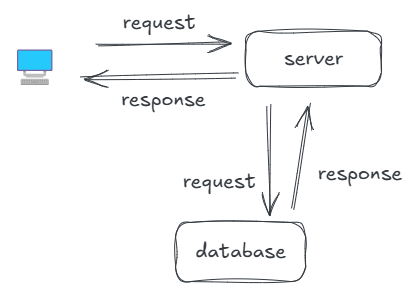
How do we distribute incoming requests across these servers ? LoadBalancer ?? HELL YEAHHH !!!
Load Balancers
 So you choose horizontal scaling and there are many servers to which 100's of requests can be passed on . But what if a server ends up recieving more requests than others ?
So you choose horizontal scaling and there are many servers to which 100's of requests can be passed on . But what if a server ends up recieving more requests than others ?
To manage the request we use load balancers to distribute requests among the servers so that no signle server can get huge number of requests. If any of the server is down load balancer will only redirect traffic to healthy servers
Load Balancer Algorithms : there are several algorithms to distribute the traffic to the healthy servers.
- Least Connection : Sends request to server with the fewest active connections. By continuously monitoring the number of active connections on each server, this algorithm adapts in real-time to shifting traffic patterns and workloads, making it particularly effective when handling sessions or tasks that require varying processing times.
- Round Robin : This algorithm cycles through a list server sequentially, each server is assigned a request in turn, ensuring an equal distribution of traffic over time. While this algorithm does not take into account the current load or capacity of individual servers, it works well in scenarios where all servers have similar processing capabilities and are equally equipped to handle requests.
There are many more interesting topics related to Load Balancing for example, What is IP Hashing technique ?, What is StandBy Load Balancers ? all these will be covered in the blog Do you know Load Balancers well ??
Everything is going fine we have a large user base, a load balancer which can redirect traffic . But we get to notice there are request for the same data from our database. Can we optimize it ?? Can we do something to make client not wait much for response from our db ?? HELL YEAHHH !!
Caching
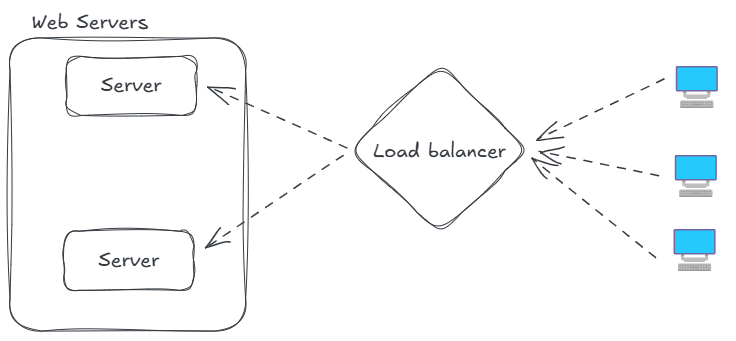
For a general context caching is like keeping frequently used items on your desk instead of fetching them from a storage room. Caching stores frequently accessed data in a temporary, high-speed storage layer, reducing latency and improving performance by minimizing redundant computations or database queries. It enhances scalability and user experience, it reduces database load and speeds up responses.
But with caching comes a problem of maintaining the data consistency of cache and the database, we should not source the data from cache if its not up-to-date with the database. What to do now ?? How are we going to update both the source of data and the cache ??
- Time Based Expiration : Cache entries are invalidated after a set time period (Time-to-Live), ensuring data is refreshed periodically
- Write Through : Data is written to the cache and backend simultaneously, ensuring consistency but with higher write latency.
We also have many interesting topics to cover for more about Caching invalidation strategies and Cache Eviction Policies which we will cover in upcoming blogs !!
Now, LeetSys's users are spreading across the globe, and those in distant regions experience latency because our server are in the data center, we need to bring content closer to users.
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
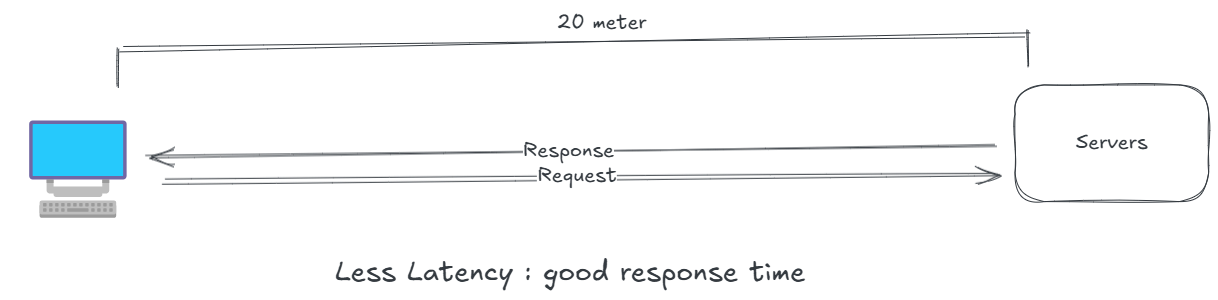

To reduce latency, we integrate a Content Delivery Network (CDN). CDNs are networks of geographically distributed servers (edge servers) that cache static content like images, videos, and CSS files closer to users. When a user in Tokyo accesses LeetSys, the CDN’s Tokyo edge server delivers cached content, reducing the round-trip time to our main servers in the India CDNs rely heavily on caching
For now this is what our system has been evolved too, from a single client server request
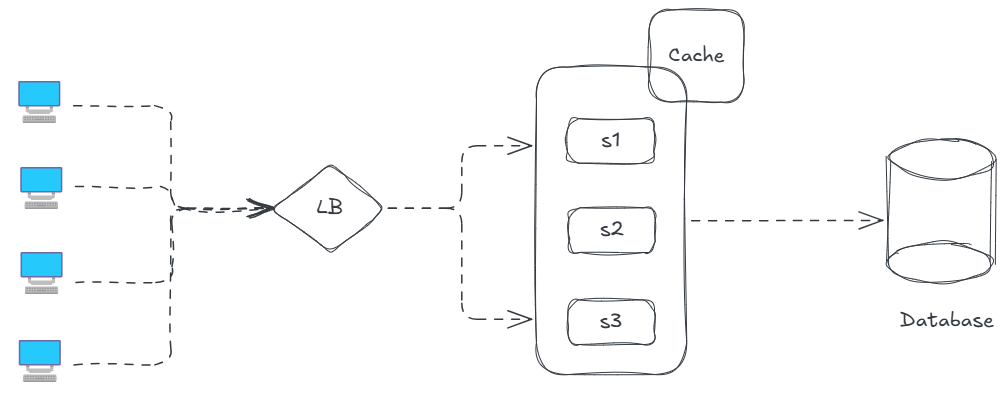 Time to focus on our Database, becuase there are many things to store now !! There are often questions asked when to choose SQL databases and when to choose NoSQL database ?? But first lets get through each of them to know in-depth
Time to focus on our Database, becuase there are many things to store now !! There are often questions asked when to choose SQL databases and when to choose NoSQL database ?? But first lets get through each of them to know in-depth
Structured Query Language (SQL)
SQL databases like PostgreSQL, Oracle, MySQL, which organizes data into tables with defined schemas, these database excel at structured data and complex queries. SQL databases scale vertically which means we need to upgrade our machine power to scale databases like this. If you had to change or add a new column the changes need to be applied to all the records in the table.
SQL has Rigid schema which will struggle with massive, unstructured data like user activity logs. For this lets explore NoSQL databases
NoSQL
NoSQL databases like MongoDB are schema-less, allowing flexible storage for documents, JSON-like for our user activity logs. They scale horizontally better than SQL but sacrifice some ACID rules for better availabiity and performance.
There are majorly 4 types of NoSQL databases
- Key Value Stores : These databases store data as key-value pairs, making them highly efficient for simple lookups and caching ex : Redis, DynamoDB
- Document Stores : These database store data as documents (often in JSON or BSON format), allowing for flexible schemas and nested structures. Ex : MongoDB, Firebase Firestore
- Column Family Stores : These database organize data into columns rather than rows, optimized for large scale data and high write/read performance. ex : Apache Cassandra
What to choose and when to choose ??
If you want strong consistency, reliability with highly structured data and consistent schema go for SQL like PostgreSQL, Oracle Database
but
If your data semi-structured, unstructured or has a dynamic schema also you want high performance with simple queries which also horizontally scales to handle massive amounts of data and high traffic you can go for NoSQL like Cassandra or Neo4j
As our user base grows we can notice a slow query performance from our backend, What to do in this situation ??
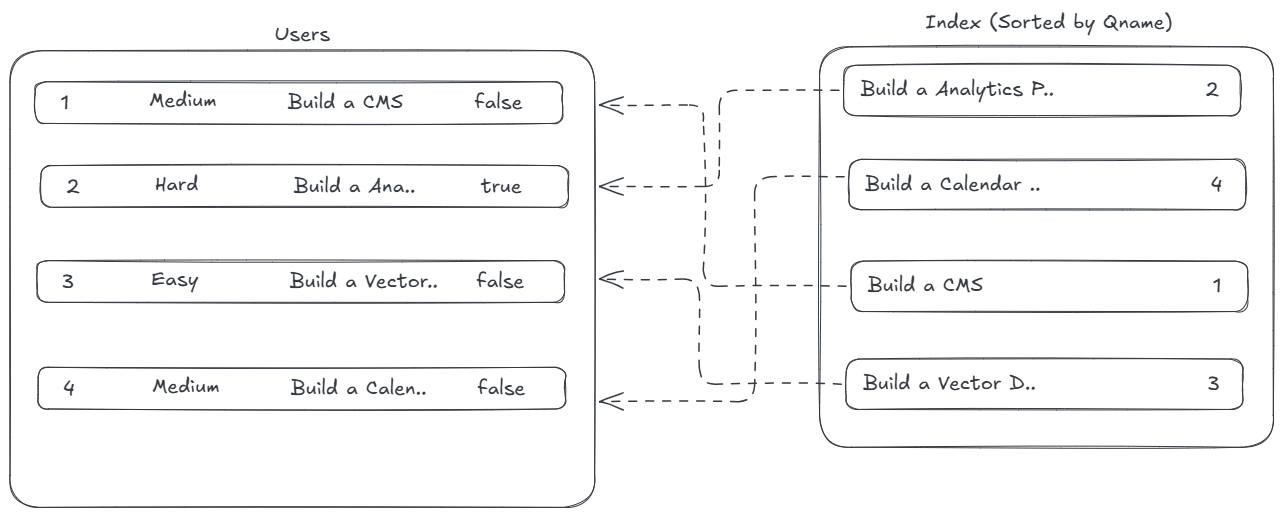
Database Indexing
Whenever there is a query our algorithm is consistently looking up from the whole database content which is making our response slow, for this we introduce Database Indexing all the primary key, or username can be indexed at a place which will help speeding up our database lookups pointing the actual location of the data.
 There's a point to which we can scale our database but after that threshold point, how we will be scaling our database to meet the requirements for our growing user base ??
There's a point to which we can scale our database but after that threshold point, how we will be scaling our database to meet the requirements for our growing user base ??
Data Partioning
When the database can no longer scale vertically then we perform data partitioning which is a technique to breakdown large databases into smaller components which enhances the performance, availabiity and load balancing as our application grows
There are mainly 4 major ways of breaking down a large database
- Horizontal Partitioning : Also known as Sharding in this the data is divided by rows, meaning each partition contains a subset of rows from the dataset. Its ideal for large datasets where different subsets of rows can be stored on separate nodes
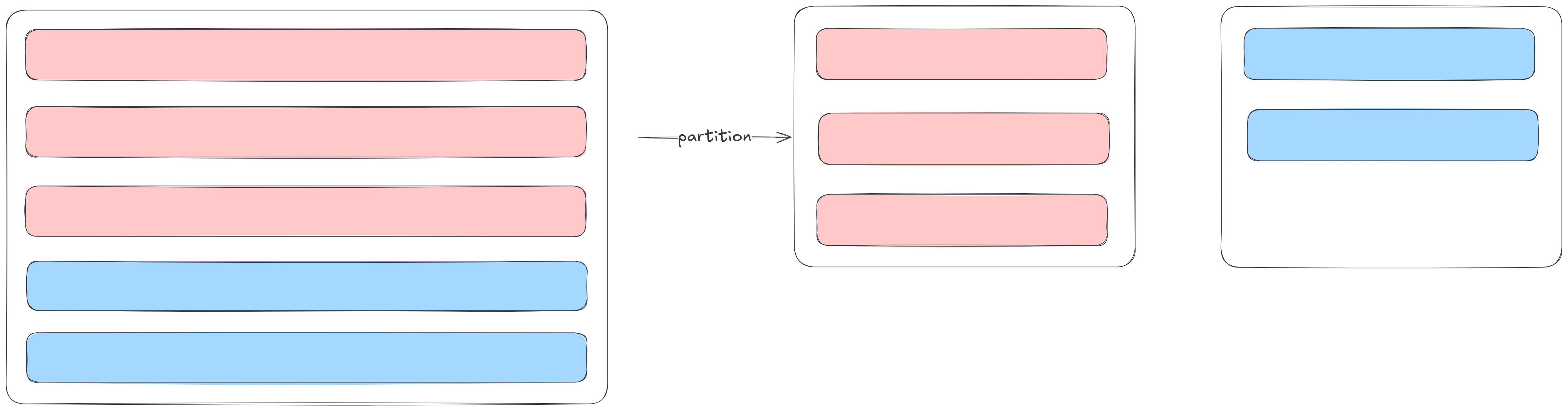 Vertical Partitioning : Data is is divided by columns, meaning each partition contains a subset of columns from the dataset, its useful when certain columns are accessed more frequently than others, allowing us to separate "Hot" (frequently accessed) and "Cold" (less frequently accessed) data. Vertical partitioning also simplifies schema design by grouping related attributes.
Vertical Partitioning : Data is is divided by columns, meaning each partition contains a subset of columns from the dataset, its useful when certain columns are accessed more frequently than others, allowing us to separate "Hot" (frequently accessed) and "Cold" (less frequently accessed) data. Vertical partitioning also simplifies schema design by grouping related attributes.
So these are the to begin our journey with system design, more often you practise questions you get to know more and more topics differenc between HLD [High Level Design] and LLD [Low Level Design]also you will get to know topics like micro services, distributed systems and more. I may write blogs on topics like this but I am leaving it to the future decesions.
This is what are system has evolved into with large user base, load balancers, cache to our web servers and database with partitioning
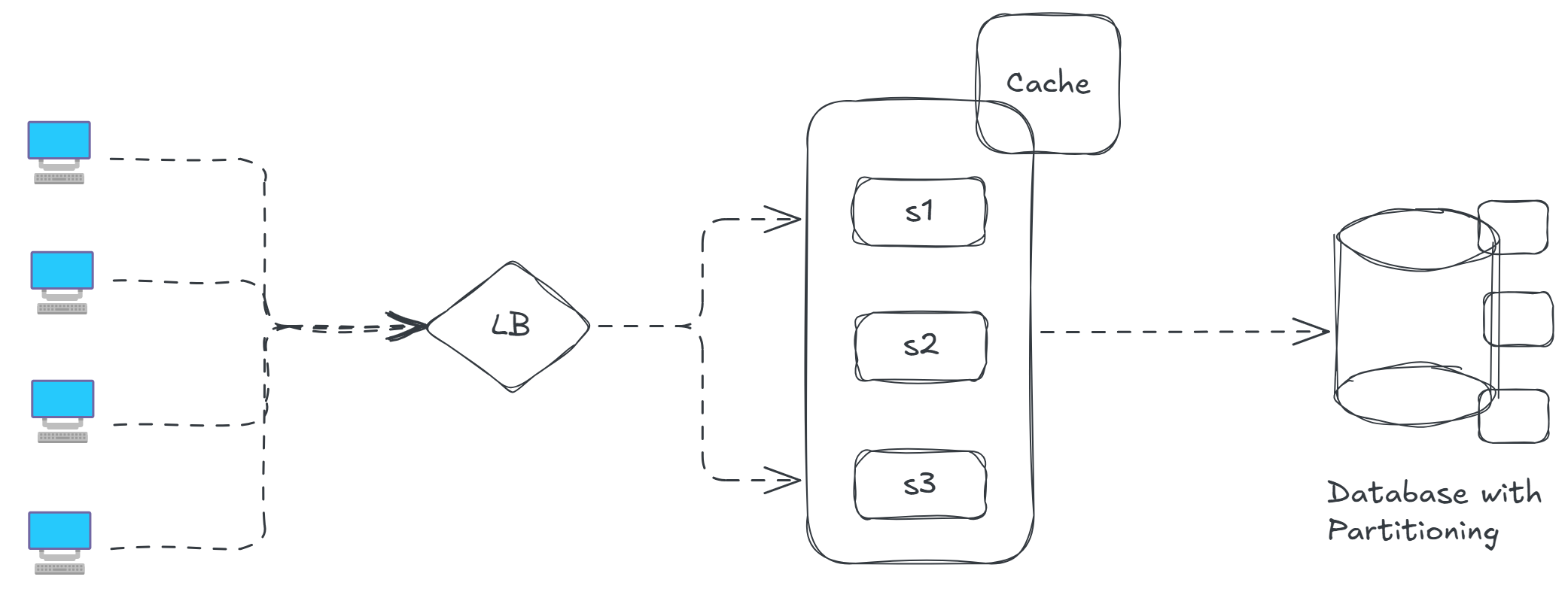 Hope I was able to add value to your today's learning goal !! Happy Learning ..
Hope I was able to add value to your today's learning goal !! Happy Learning ..